https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
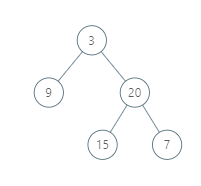
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).